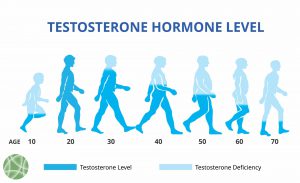
In middle age, you, as a man, or your sexual partner (keeping this observation to her/himself), will likely start to notice a group of symptoms due to a slow but inevitable decline of your male hormone testosterone. As the movie director Martin Scorsese put it well, “Sex becomes memory.” Not necessarily. Not by a long […]
Tag: heart disease prevention
Heart Disease Prevention Part 3
The (alleged) BIG NEWS in health care last week, that spread through CNN, Prevention Magazine, NYT, Journal of the AMA, etc. etc., was the publication in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology which compared the cholesterol lowering effect of statins to those of several nutritional supplements (cinnamon, fish oil, garlic, red yeast rice, […]
Heart Disease Prevention Part 2: Getting Started
Checking Your Family History Most people aren’t certain what illnesses run in their family and how dangerous these might be. Probably best not to spend much time agonizing about this, unless you’re pretty sure there was an unusually excessive amount of premature deaths (50’s, 60’s) from heart disease. Better to work mainly on yourself. Hearing […]
Covid Distracted Us, But Heart Disease Remains Our #1 Killer
About 700,000 of us will die of heart disease every year; most of which is preventable provided we become proactive patients. But you do need to know that for most “heart patients”, dying does not come quickly, like a dart falling from the sky, fatally nailing you, as you clutch your chest, your friends desperately tapping 9-1-1 on their […]
NAC (N-acetylcysteine)
Produced by the body, N-acetylcysteine (commonly called NAC) is a form of the amino acid cysteine. Because it enhances the production of the Enzyme glutathione, one of the body’s powerhouse antioxidants, NAC can both stave off disease and play an important role in boosting the immune system. Studies have shown that glutathione levels are often reduced in people with certain conditions related to the immune system.
Vitamin C
In the eighteenth century, seasoned sailors found that by sucking on lemons they could avoid scurvy, a debilitating disease that often developed during long voyages when fresh fruits and vegetables were scarce. When the lemon’s key nutrient was formally identified in 1928, it was named ascorbic acid for its anti-scurvy, or antiscorbutic, action. Today ascorbic acid is widely known as vitamin C.
Magnesium
Essential for hundreds of chemical reactions that occur in the body every second, the mineral magnesium has received surprisingly little attention over the years. Recent findings, however, suggest that it also has important health-promoting benefits, from an ability to prevent heart disease to a role in treating such chronic conditions as fibromyalgia and diabetes.
Hawthorn
Hawthorn (Crataegus oxyacantha), a rose family member popularly planted along hedges to deter trespassers with its prickly branches, has heart-healthy properties that ancient Greeks and Native Americans recognized centuries ago. Its modern reputation as a healing agent dates to Victorian times, when an Irish physician’s secret heart formula was ultimately revealed to contain a tincture made from the bright red berries.
Flaxseed Oil
A source of fiber for linen fabric since ancient times, the slender flax plant (Linum usitatissimum) also boasts a long history as a healing herb. First cultivated in Europe, the plant’s brown seeds were regularly used to prepare balms for inflamed skin and healing slurries for constipation. Today, flaxseeds–also called linseeds–are best known for the therapeutic oil that is derived by pressing them. Rich in essential fatty acids, or EFAs, flaxseed oil has earned a solid reputation for treating a range of ailments, from heart disease to lupus.
Flavinoids
Flavonoids is the umbrella term given to some 4,000 compounds that impart the colorful pigment to fruits, vegetables and herbs. Also found in legumes, grains and nuts, flavonoids can act as effective antivirals, anti-inflammatories, antihistamines and antioxidants. They’re useful for reducing cancer risk and serve to prevent or treat a wide variety of conditions.
Copper
Copper is the third most abundant trace mineral in the human body. Most Americans readily identify it as the dark reddish, malleable metal used in cookware and plumbing. Numerous foods contain copper, although the particularly rich sources such as liver and oysters are not commonly consumed. In fact, most Americans get too little of this important nutrient.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
One of the world’s most popular supplements, the chemical coenzyme Q10 has generated great excitement as a heart disease remedy and a cure for countless other conditions. The body naturally produces this compound, which has been dubbed “vitamin Q” because of its essential role in keeping all systems running smoothly. In fact, the scientists who identified coenzyme Q10 in 1957 initially honored its ubiquitous presence–it’s found in every human cell and in all living organisms–by naming it “ubiquinone.” Small amounts are also present in most foods.
Carotenoids
Carotenoids are the pigments that color some fruits and vegetables red, orange and yellow. Recent research has shown that, acting as antioxidants, these natural plant compounds can boost the immune system and possibly lower the risk of heart disease, prevent the onset of some cancers, and protect against such age-related diseases as cataracts and macular degeneration.
Alpha-Linolenic Acid
Alpha-linolenic acid is an essential fatty acid and the major omega-3 fatty acid found in food. Essential fatty acids are not produced by the body and must be present in the diet to maintain health. The unique biochemical structure of alpha-linolenic acid is important and helps to make it a key player in immunity, vision, cell membranes, and the production of hormonelike compounds.
Allium Compounds
Allium compounds are derived from Allium sativum, or garlic, which is one of the most widely studied medicinal plants. The fresh garlic bulb is usually dried, crushed into a powder, and then compressed to produce a tablet. The tablet form is the most commonly used commercial preparation of garlic. Raw whole cloves have similar effects.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a new and very popular supplement currently recommended by nutritionally oriented physicians, including myself, as avery potent antioxidant that may have potential as an anticancer and cardioprotective compound..
Resveratrol is found in the skins of red grapes and is, therefore, a component of red wine. It is also found in purple grape juice, berries such as blueberries, cranberries, and raspberries, and in smaller amounts in peanuts. In the 1990s, the compound began to attract attention as an explanation of the so-called “French paradox,” namely the low incidence of heart disease among French people despite their diet high in saturated fats.
Is Vitamin C Worthwhile?
I’m asked this question a lot.
You’d think the controversy would be over by now. Among doctors who take vitamins regularly (now the majority), vitamin C is always included.